Les investisseurs et les actionnaires reconnaissent le rôle prioritaire que les administrateurs de sociétés jouent dans la gouvernance et, conséquemment, ils veulent toujours plus d’informations sur le processus de nomination des administrateurs et sur la composition du conseil d’administration.
L’article qui suit, paru sur le Forum du Harvard Law School, a été publié par Paula Loop, directrice du centre de la gouvernance de PricewaterhouseCoopers. Il s’agit essentiellement d’un compte rendu sur l’évolution des facteurs clés de la composition des conseils d’administration. La présentation s’appuie sur une infographie remarquable.
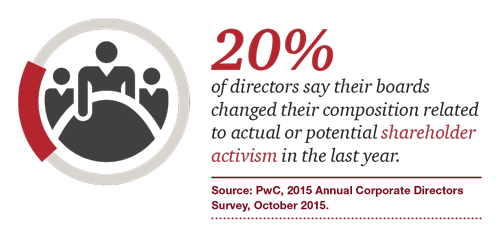
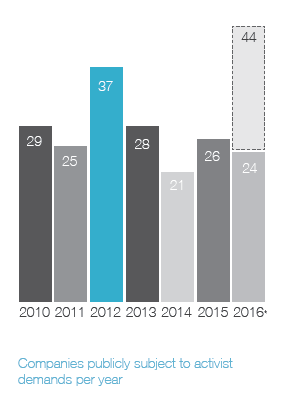
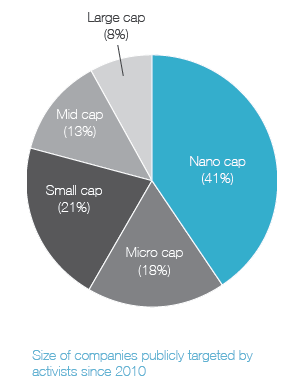
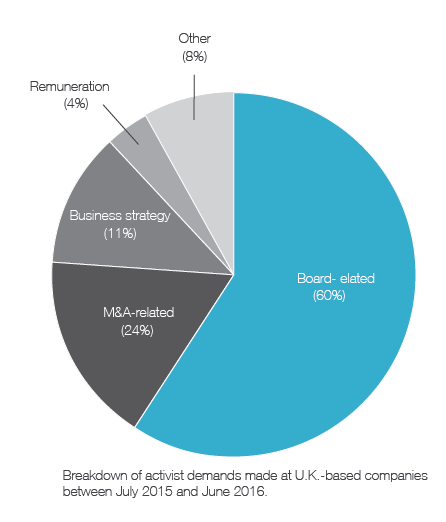
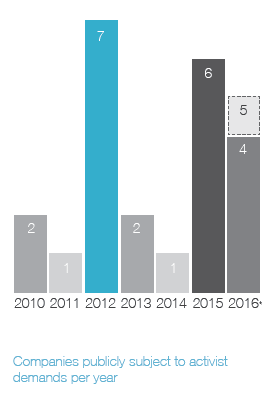
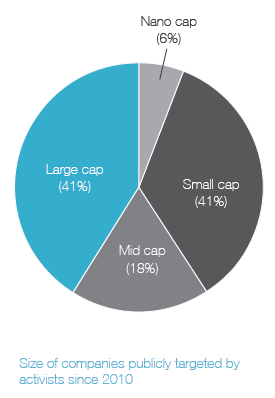
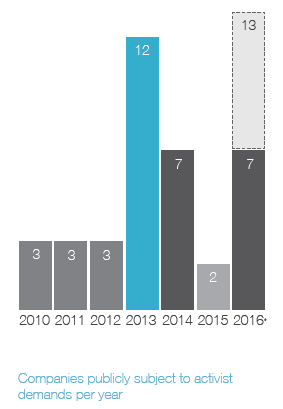
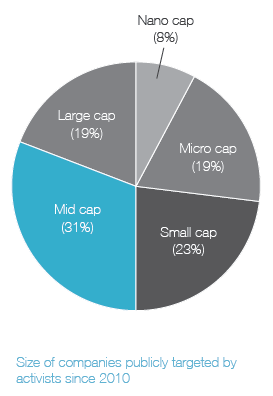
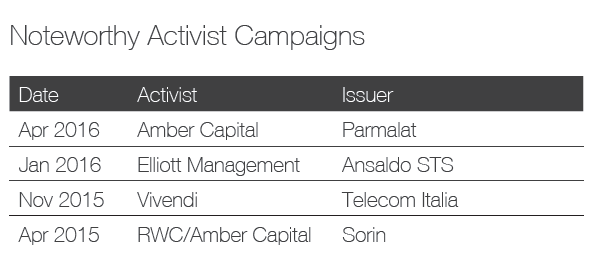
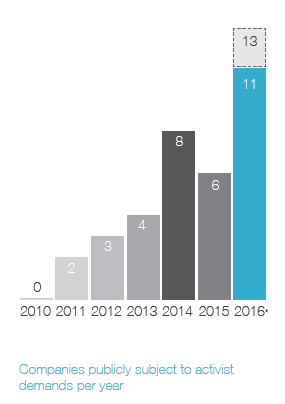
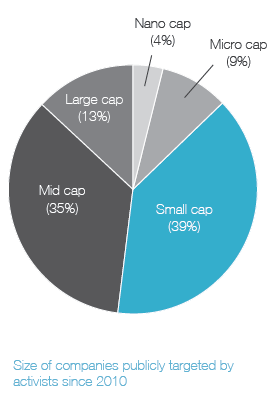
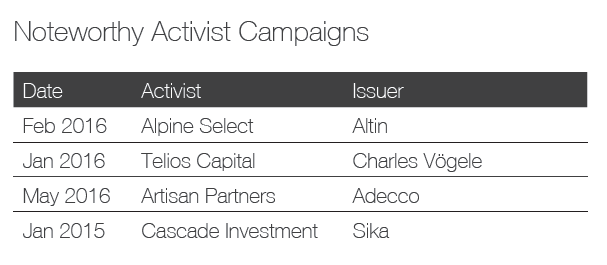
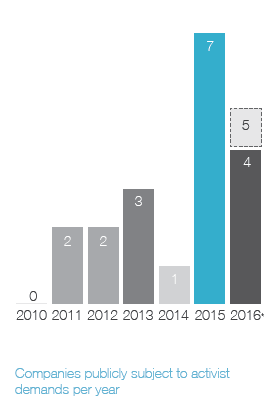
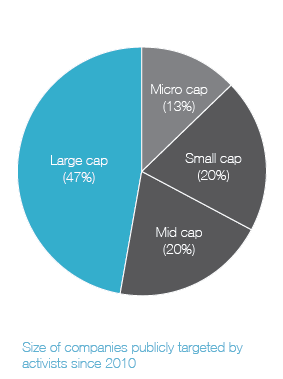
Ainsi, on apprend que 41 % des campagnes menées par les activistes étaient reliées à la composition des CA, et que 20 % des CA ont modifié leur composition en réponse aux activités réelles ou potentielles des activistes.
L’article s’attarde sur la grille de composition des conseils relative aux compétences et habiletés requises. Également, on présente les arguments pour une plus grande diversité des CA et l’on s’interroge sur la situation actuelle.
Enfin, l’article revient sur les questions du nombre de mandats des administrateurs et de l’âge de la retraite de ceux-ci ainsi que sur les préoccupations des investisseurs eu égard au renouvellement et au rajeunissement des CA.
Le travail de renouvellement du conseil ne peut se faire sans la mise en place d’un processus d’évaluation complet du fonctionnement du CA et des administrateurs.
À mon avis, c’est certainement un article à lire pour bien comprendre toutes les problématiques reliées à la composition des conseils d’administration.
Bonne lecture !
Investors and Board Composition
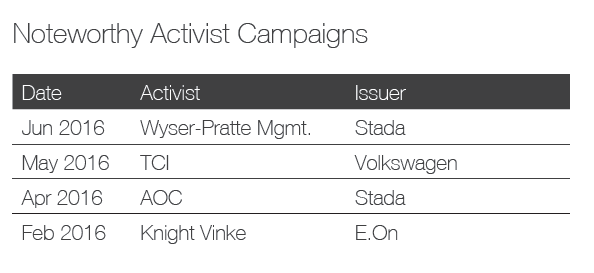
In today’s business environment, companies face numerous challenges that can impact success—from emerging technologies to changing regulatory requirements and cybersecurity concerns. As a result, the expertise, experience, and diversity of perspective in the boardroom play a more critical role than ever in ensuring effective oversight. At the same time, many investors and other stakeholders are seeking influence on board composition. They want more information about a company’s director nominees. They also want to know that boards and their nominating and governance committees are appropriately considering director tenure, board diversity and the results of board self-evaluations when making director nominations. All of this is occurring within an environment of aggressive shareholder activism, in which board composition often becomes a central focus.
Shareholder activism and board composition
At the same time, a growing number of companies are adopting proxy access rules—allowing shareholders that meet certain ownership criteria to submit a limited number of director candidates for inclusion on the company’s annual proxy. It has become a top governance issue over the last two years, with many shareholders viewing it as a step forward for shareholder rights. And it’s another factor causing boards to focus more on their makeup.
So within this context, how should directors and investors be thinking about board composition, and what steps should be taken to ensure boards are adequately refreshing themselves?
Assessing what you have–and what you need
In a rapidly changing business climate, a high-performing board requires agile directors who can grasp concepts quickly. Directors need to be fiercely independent thinkers who consciously avoid groupthink and are able to challenge management—while still contributing to a productive and collegial boardroom environment. A strong board includes directors with different backgrounds, and individuals who understand how the company’s strategy is impacted by emerging economic and technological trends.
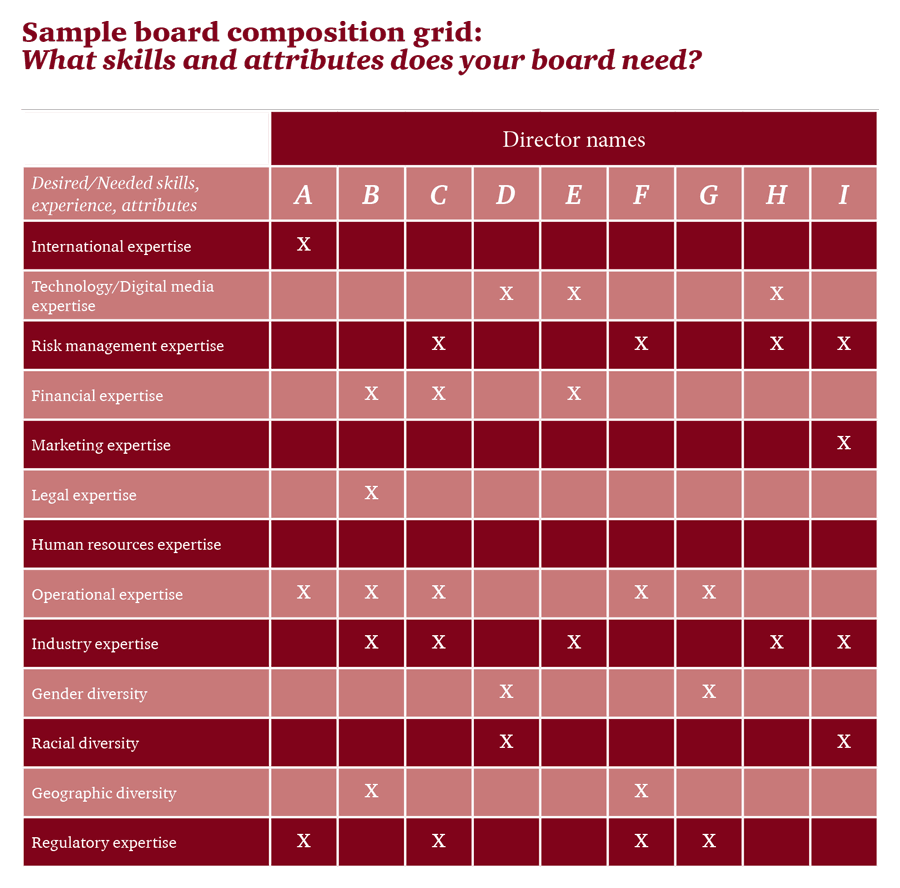
Sample board composition grid: What skills and attributes does your board need?
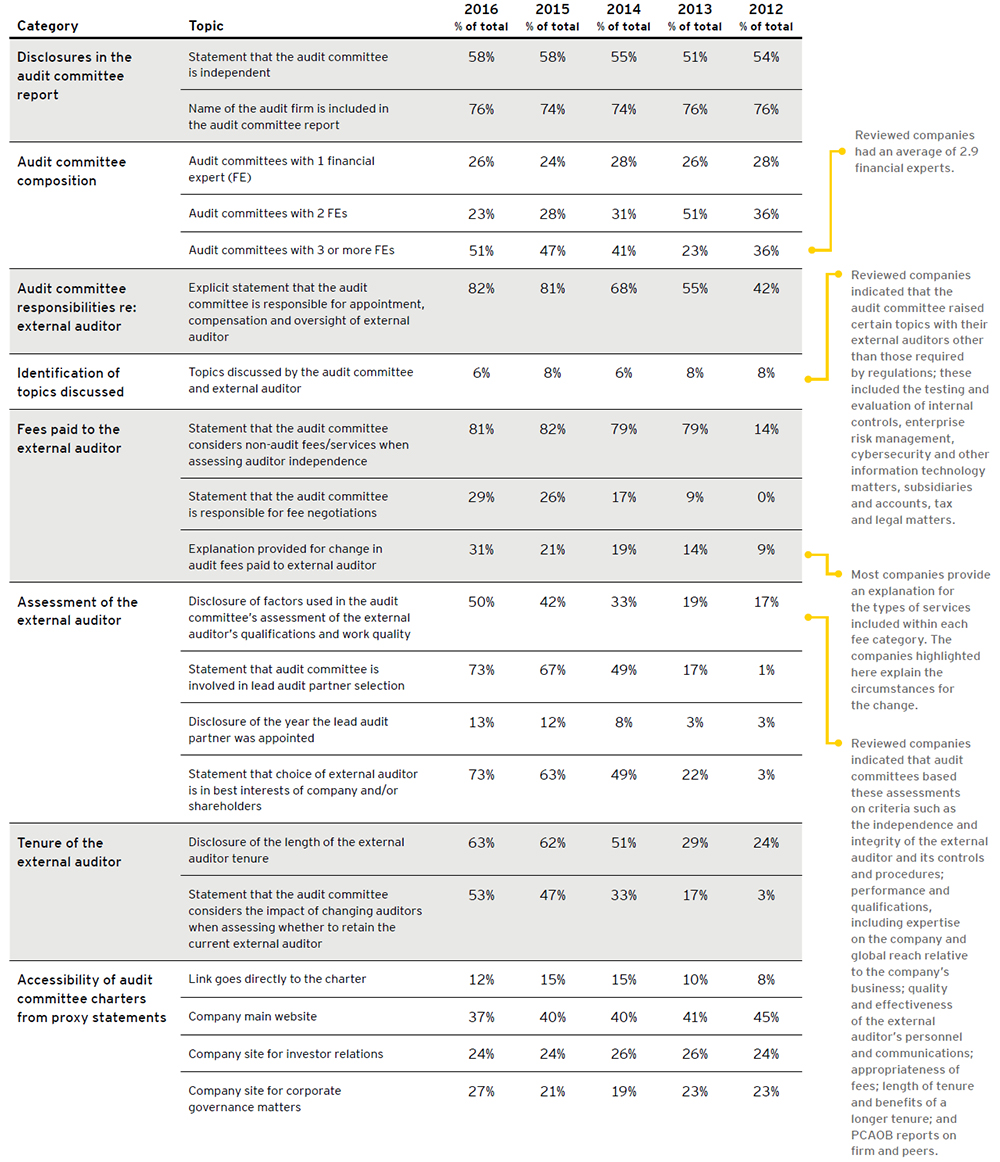
In assessing their composition, boards and their nominating and governance committees need to think critically about what skills and attributes the board currently has, and how they tie to oversight of the company. As companies’ strategies change and their business models evolve, it is imperative that board composition be evaluated regularly to ensure that the right mix of skills are present to meet the company’s current needs. Many boards conduct a gap analysis that compares current director attributes with those that it has identified as critical to effective oversight. They can then choose to fill any gaps by recruiting new directors with such attributes or by consulting external advisors. Some companies use a matrix in their proxy disclosures to graphically display to investors the particular attributes of each director nominee.
Board diversity is a hot-button issue
Diversity is a key element of any discussion of board composition. Diversity includes not only gender, race, and ethnicity, but also diversity of skills, backgrounds, personalities, opinions, and experiences. But the pace of adding more gender and ethnic diversity to public company boards has been only incremental over the past five years. For example, a December 2015 report from the US Government Accountability Office estimates that it could take four decades for the representation of women on US boards to be the same as men. [1] Some countries, including Norway, Belgium, and Italy, have implemented regulatory quotas to increase the percentage of women on boards.
Even if equal proportions of women and men joined boards each year beginning in 2015, GAO estimated that it could take more than four decades for women’s representation on boards to be on par with that of men’s.
—US Government Accountability Office, December 2015According to PwC’s 2015 Annual Corporate Directors Survey, more than 80% of directors believe board diversity positively impacts board and company performance. But more than 70% of directors say there are impediments to increasing board diversity. [2] One of the main impediments is that many boards look to current or former CEOs as potential director candidates. However, only 4% of S&P 500 CEOs are female, [3] less than 2% of the Fortune 500 CEOs are Hispanic or Asian, and only 1% of the Fortune 500 CEOs are African-American. [4] So in order to get boards to be more diverse, the pool of potential director candidates needs to be expanded.
Is there diversity on US boards?
Source: Spencer Stuart US Board Index 2015, November 2015.
SEC rules require companies to disclose the backgrounds and qualifications of director nominees and whether diversity was a nomination consideration. In January 2016, SEC Chair Mary Jo White included diversity as a priority for the SEC’s 2016 agenda and suggested that the SEC’s disclosure rules pertaining to board diversity may be enhanced.
While those who aspire to become directors must play their part, the drive to make diversity a priority really has to come from board leadership: CEOs, lead directors, board chairs, and nominating and governance committee chairs. These leaders need to be proactive and commit to making diversity part of the company and board culture. In order to find more diverse candidates, boards will have to look in different places. There are often many untapped, highly qualified, and diverse candidates just a few steps below the C-suite, people who drive strategies, run large segments of the business, and function like CEOs.
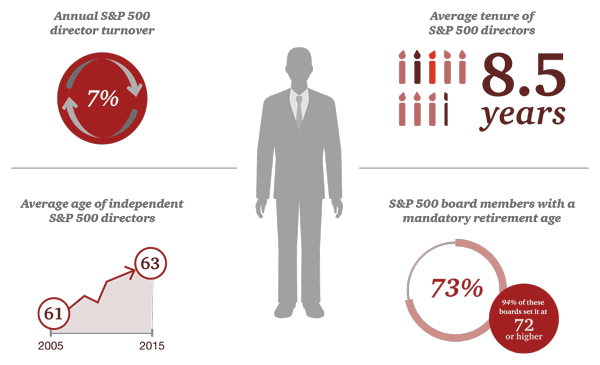
How long is too long? Director tenure and mandatory retirement
The debate over board tenure centers on whether lengthy board service negatively impacts director independence, objectivity, and performance. Some investors believe that long-serving directors can become complacent over time—making it less likely that they will challenge management. However, others question the virtue of forced board turnover. They argue that with greater tenure comes good working relationships with stakeholders and a deep knowledge of the company. One approach to this issue is to strive for diversity of board tenure—consciously balancing the board’s composition to include new directors, those with medium tenures, and those with long-term service.
This debate has heated up in recent years, due in part to attention from the Council of Institutional Investors (the Council). In 2013, the Council introduced a revised policy statement on board tenure. While the policy “does not endorse a term limit,” [5] the Council noted that directors with extended tenures should no longer be considered independent. More recently, the large pension fund CalPERS has been vocal about tenure, stating that extended board service could impede objectivity. CalPERS updated its 2016 proxy voting guidelines by asking companies to explain why directors serving for over twelve years should still be considered independent.
We believe director independence can be compromised at 12 years of service—in these situations a company should carry out rigorous evaluations to either classify the director as non-independent or provide a detailed annual explanation of why the director can continue to be classified as independent.
— CalPERS Global Governance Principles, second reading, March 14, 2016Factors in the director tenure and age debate
Source: Spencer Stuart US Board Index 2015, November 2015.
Many boards have a mandatory retirement age for their directors. However, the average mandatory retirement age has increased in recent years. Of the 73% of S&P 500 boards that have a mandatory retirement age in place, 97% set that age at 72 or older—up from 57% that did so ten years ago. Thirty-four percent set it at 75 or older. [6] Others believe that director term limits may be a better way to encourage board refreshment, but only 3% of S&P 500 boards have such policies. [7]
Investor concern
Some institutional investors have expressed concern about board composition and refreshment, and this increased scrutiny could have an impact on proxy voting decisions.
What are investors saying about board composition and refreshment?
Sources: BlackRock, Proxy voting guidelines for U.S. securities, February 2015; California Public Employees’ Retirement System, Statement of Investment Policy for Global Governance, March 16, 2015; State Street Global Advisors’ US Proxy Voting and Engagement Guidelines, March 2015.
Proxy advisors’ views on board composition—recent developments
Proxy advisory firm Institutional Shareholder Services’s (ISS) governance rating system QuickScore 3.0 views tenure of more than nine years as potentially compromising director independence. ISS’s 2016 voting policy updates include a clarification that a “small number” of long-tenured directors (those with more than nine years of board service) does not negatively impact the company’s QuickScore governance rating, though ISS does not provide specifics on the acceptable quantity.
Glass Lewis’ updated 2016 voting policies address nominating committee performance. Glass Lewis may now recommend against the nominating and governance committee chair “where the board’s failure to ensure the board has directors with relevant experience, either through periodic director assessment or board refreshment, has contributed to a company’s poor performance.” Glass Lewis believes that shareholders are best served when boards are diverse on the basis of age, race, gender and ethnicity, as well as on the basis of geographic knowledge, industry experience, board tenure, and culture.
How can directors proactively address board refreshment?
The first step in refreshing your board is deciding whether to add a new board member and determining which director attributes are most important. One way to do this is to conduct a self-assessment. Directors also have a number of mechanisms to address board refreshment. For one, boards can consider new ways of recruiting director candidates. They can take charge of their composition through active and strategic succession planning. And they can also use robust self-assessments to gauge individual director performance—and replace directors who are no longer contributing.
- Act on the results of board assessments. Boards should use their annual self-assessment to help spark discussions about board refreshment. Having a robust board assessment process can offer insights into how the board is functioning and how individual directors are performing. The board can use this process to identify directors that may be underperforming or whose skills may no longer match what the company needs. It’s incumbent upon the board chair or lead director and the chair of the nominating and governance committee to address any difficult matters that may arise out of the assessment process, including having challenging conversations with underperforming directors. In addition, some investors are asking about the results of board assessments. CalPERS and CalSTRS have both called on boards to disclose more information about the impact of their self-assessments on board composition decisions. [8]
- Take a strategic approach to director succession planning. Director succession planning is essential to promoting board refreshment. But, less than half of directors “very much” believe their board is spending enough time on director succession. [9] In board succession planning, it’s important to think about the current state of the board, the tenure of current members, and the company’s future needs. Boards should identify possible director candidates based upon anticipated turnover and director retirements.
- Broaden the pool of candidates. Often, boards recruit directors by soliciting recommendations from other sitting directors, which can be a small pool. Forward-looking boards expand the universe of potential qualified candidates by looking outside of the C-suite, considering investor recommendations, and by looking for candidates outside the corporate world—from the retired military, academia, and large non-profits. This will provide a broader pool of individuals with more diverse backgrounds who can be great board contributors.
In sum, evaluating board composition and refreshing the board may be challenging at times, but it’s increasingly a topic of concern for many investors, and it’s critical to the board’s ability to stay current, effective, and focused on enhancing long-term shareholder value.
The complete publication, including footnotes and appendix, is available here.
Endnotes:
[1] United States Government Accountability Office, “Corporate Boards: Strategies to Address Representation of Women Include Federal Disclosure Requirements,” December 2015.
(go back)[2] PwC, 2015 Annual Corporate Directors Survey, October 2015.
(go back)[3] Catalyst, Women CEOs of the S&P 500, February 3, 2016.
(go back)[4] “McDonald’s CEO to Retire; Black Fortune 500 CEOs Decline by 33% in Past Year,” DiversityInc, January 29, 2015; http://www.diversityinc.com/leadership/mcdonalds-ceo-retire-black-fortune-500-ceos-decline-33-past-year.
(go back)[5] Amy Borrus, “More on CII’s New Policies on Universal Proxies and Board Tenure,” Council of Institutional Investors, October 1, 2013; http://www.cii.org/article_content.asp?article=208.
(go back)[6] Spencer Stuart, 2015 US Board Index, November 2015.
(go back)[7] Spencer Stuart, 2015 US Board Index, November 2015.
(go back)[8] California State Teachers’ Retirement System Corporate Governance Principles, April 3, 2015, http://www.calstrs.com/sites/main/files/file-attachments/corporate_governance_principles_1.pdf; The California Public Employees’ Retirement System Global Governance Principles, Updated March 14, 2016, https://www.calpers.ca.gov/docs/board-agendas/201603/invest/item05a-02.pdf.
(go back)[9] PwC, 2015 Annual Corporate Directors Survey, October 2015. www.pwc.com/us/GovernanceInsightsCenter.
________________________________
*Paula Loop is Leader of the Governance Insights Center at PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP. This post is based on a PwC publication by Ms. Loop and Paul DeNicola. The complete publication, including footnotes and appendix, is available here.