Comment a évolué la situation du statut d’indépendance des administrateurs en 2017 ?
La publication d’EY est très intéressante à cet égard ; elle tente de répondre à cette question et elle brosse un tableau de la composition des conseils d’administration en 2017.
L’étude effectuée par l’équipe de Steve W. Klemash* auprès des entreprises du Fortune 100 montre clairement l’importance accrue accordée au critère d’administrateur indépendant au fil des ans.
Ainsi, au cours des deux dernières années, 80 % des administrateurs nommés par les actionnaires avaient la qualité d’administrateurs indépendants.
La plupart des nouveaux administrateurs avaient une expertise en finance et comptabilité et 44 % de ceux-ci ont été nommés sur le comité d’audit.
Cette année, 54 % des nouveaux arrivants étaient des personnes qui n’étaient pas CEO, comparativement à 51 % l’année précédente.
On compte 40 % de femmes parmi les nouveaux administrateurs en 2017.
Également, les nouveaux administrateurs sont plus jeunes : 15 % ont moins de 50 ans comparativement à 9 % l’année précédente. De plus, 85 % des nouveaux administrateurs avaient entre 50 ans et 67 ans.
Les entreprises recherchent une plus grande diversité de profils d’origine, d’expertises, d’habiletés et d’expériences.
J’ai tenté de résumer les principales conclusions de cette étude. Je vous renvoie à l’étude originale afin d’en connaître les détails.
Bonne lecture ! Vos commentaires sont les bienvenus.
Independent Directors: New Class of 2017
Companies are continuing to bring fresh and diverse perspectives into the boardroom and to enhance alignment of board composition with their forward-looking strategies.
In our second annual report, we share the results of our analysis of independent directors who were elected by shareholders to the board of a Fortune 100 company for the first time in 2017—what we refer to as the “new class of 2017.”
We looked at corporate disclosures to see what qualifications and characteristics were specifically highlighted, showcasing what this new class of directors brings to the boardroom. Our research was based on a review of proxy statements filed by companies on the 2017 Fortune 100 list. We also reviewed the same 83 companies’ class of 2016 directors to provide consistency in year-on-year comparisons.
Our perspective
What we’re hearing in the market is that boards are seeking slates of candidates who bring a diverse perspective and a range of functional expertise, including on complex, evolving areas such as digital transformation, e-commerce, public policy, regulation and talent management. As a result, boards are increasingly considering highly qualified, nontraditional candidates, such as non-CEOs, as well as individuals from a wider range of backgrounds. These developments are expanding the short lists of potential director candidates.
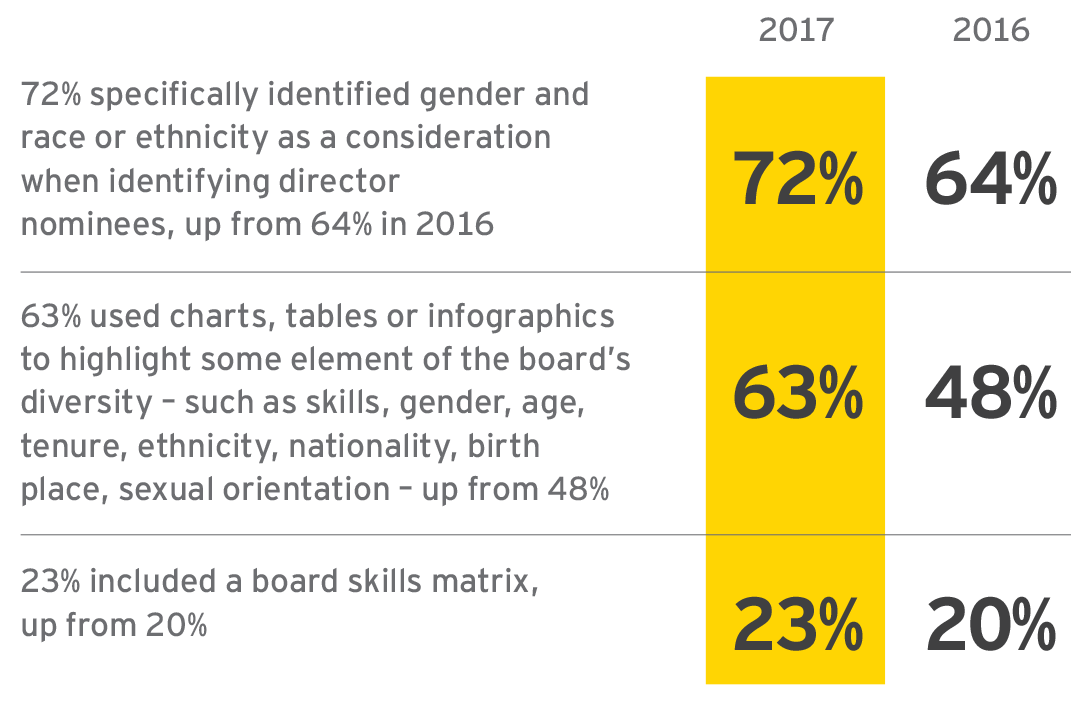
At the same time, companies are expanding voluntary disclosures around board composition. Our review of Fortune 100 disclosures around board composition found that:
While diverse director candidates are in high demand and related shifts in board composition are underway, these developments may be slow to manifest. For example, consider that the average Fortune 100 board has 10 seats. In this context, the addition of a single new director is unlikely to dramatically shift averages in terms of gender diversity, age, tenure or other considerations.
That said, whether a board’s pace of change is sufficient depends on a company’s specific circumstances and evolving board oversight needs. Boards should challenge their approach to refreshment, asking whether they are meeting the company’s diversity, strategy and risk oversight needs. Waiting for an open seat to nominate a diverse candidate may mean waiting for the value that diversity could bring.
In 2018, we anticipate that companies will continue to offer more voluntary disclosure on board composition, showing how their directors represent the best mix of individuals for the company—across multiple dimensions, including a diversity of backgrounds, expertise, skill sets and experiences.
Key findings
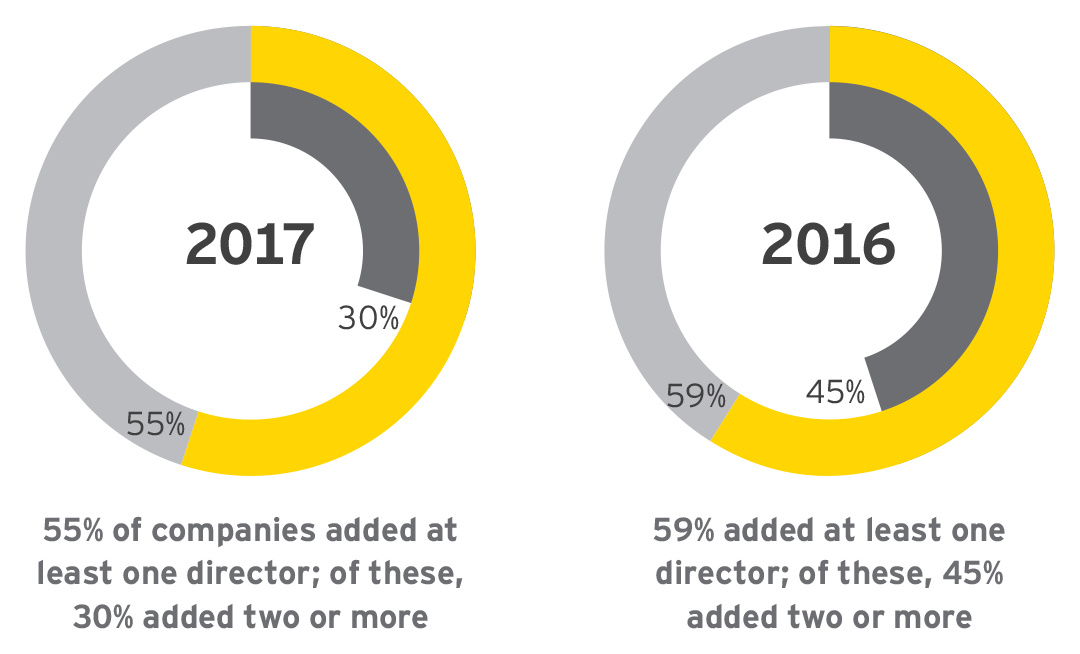
1. Most Fortune 100 companies welcomed a new independent director in 2017
This past year, over half of the Fortune 100 companies we reviewed added at least one independent director. This figure is a little lower than the prior year; but overall, during the two-year period from 2016 to 2017, over 80% of the companies added at least one independent director. Taking into account director exits—whether due to retirement, corporate restructuring, pursuit of new opportunities or other reasons—we found that nearly all of the companies experienced some type of change in board composition during this period.
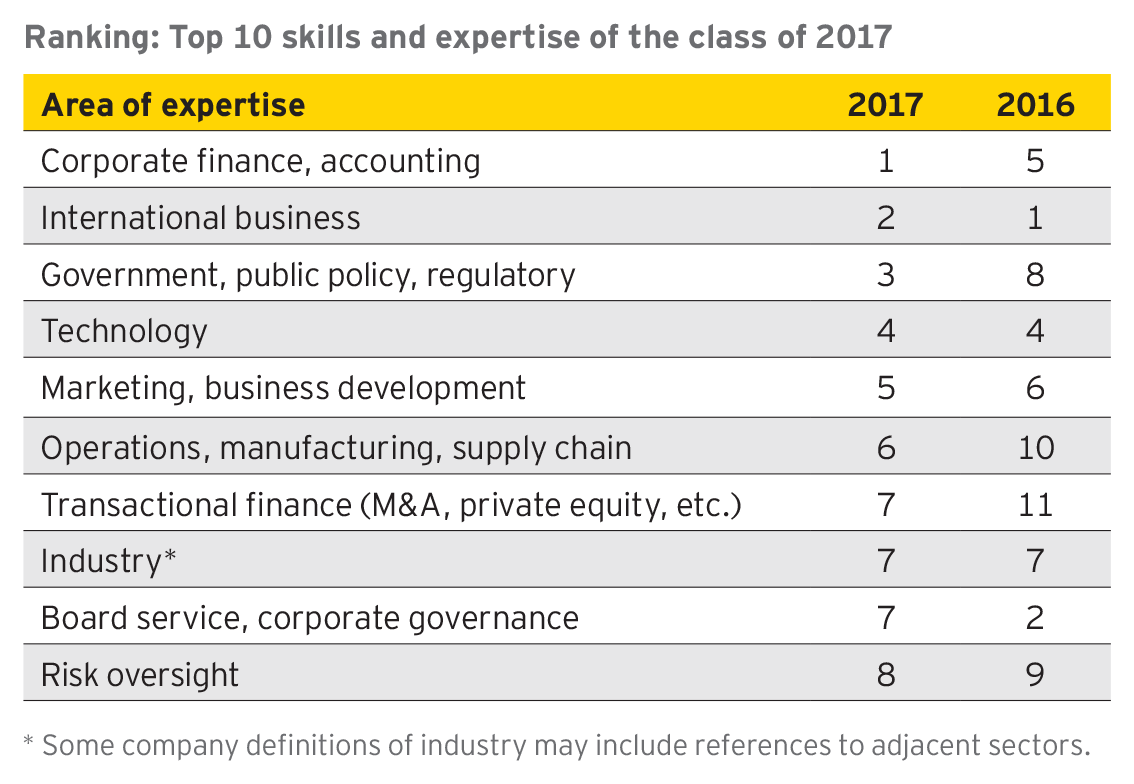
2. The class of 2017 brings greater finance and accounting, public policy and regulatory, and operational skills to the table.
Corporate finance and accounting were the most common director qualifications cited by companies in 2017, up from fifth in 2016. A couple areas saw notable increases: government and public policy, operations and manufacturing, and transactional finance. This year, some areas tied in ranking, and in a twist, corporate references to expertise in strategy fell from third in 2016 to below the top 10 categories of expertise. Companies also made fewer references to board service or governance expertise compared to the prior year.
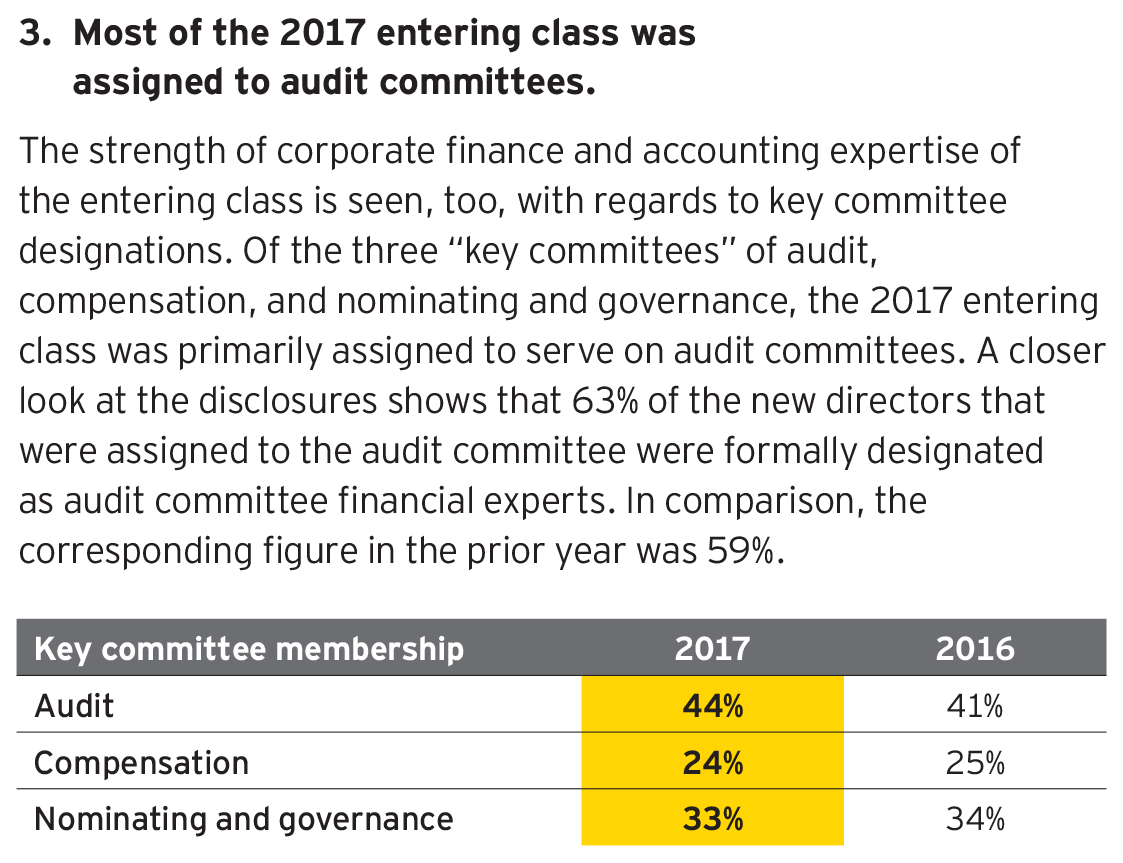
3. Most of the 2017 entering class was assigned to audit committees.
The strength of corporate finance and accounting expertise of the entering class is seen, too, with regards to key committee designations. Of the three “key committees” of audit, compensation, and nominating and governance, the 2017 entering class was primarily assigned to serve on audit committees. A closer look at the disclosures shows that 63% of the new directors that were assigned to the audit committee were formally designated as audit committee financial experts. In comparison, the corresponding figure in the prior year was 59%.
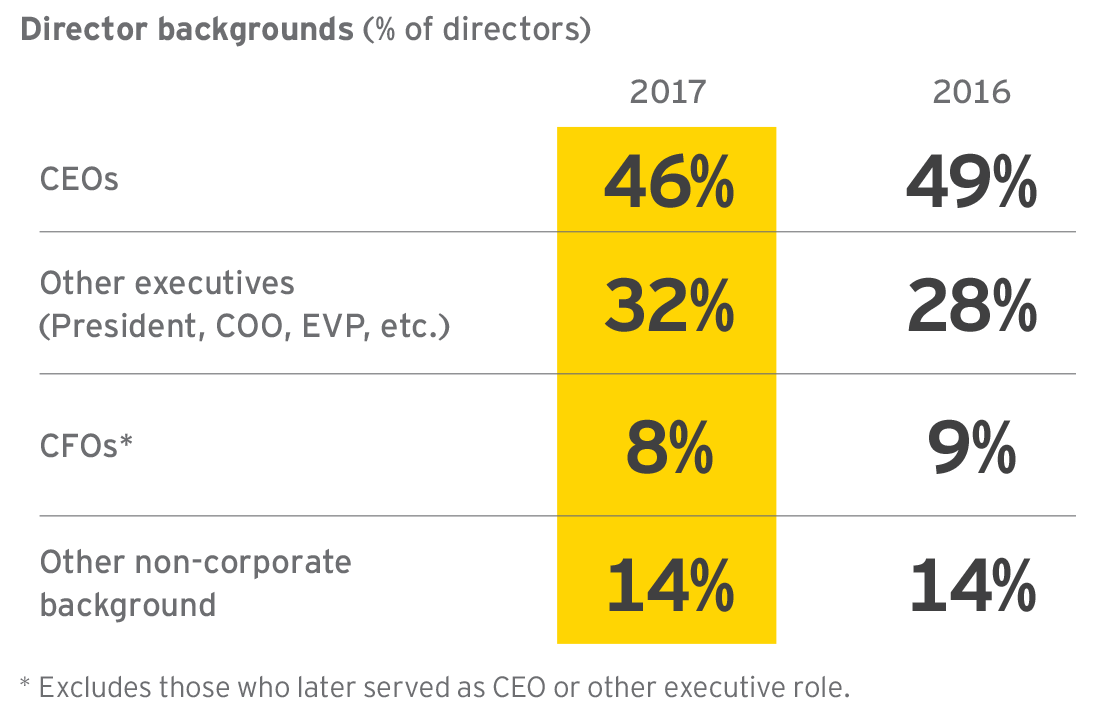
4. The Fortune 100 class of 2017 includes more non-CEOs.
While experience as a CEO is often cited as a traditional first cut for search firms, 54% of the entering class served in other roles, with non-CEO backgrounds including other executive roles or non-corporate backgrounds (academia, scientific organizations, nonprofits, government, military, etc.). This represents a slight increase from 2016 with most of the shift stemming from individuals holding or having held other senior executive positions. Approximately 30% appear to be joining a Fortune 100 public company board, having never previously served on a public company board—similar to 2016.
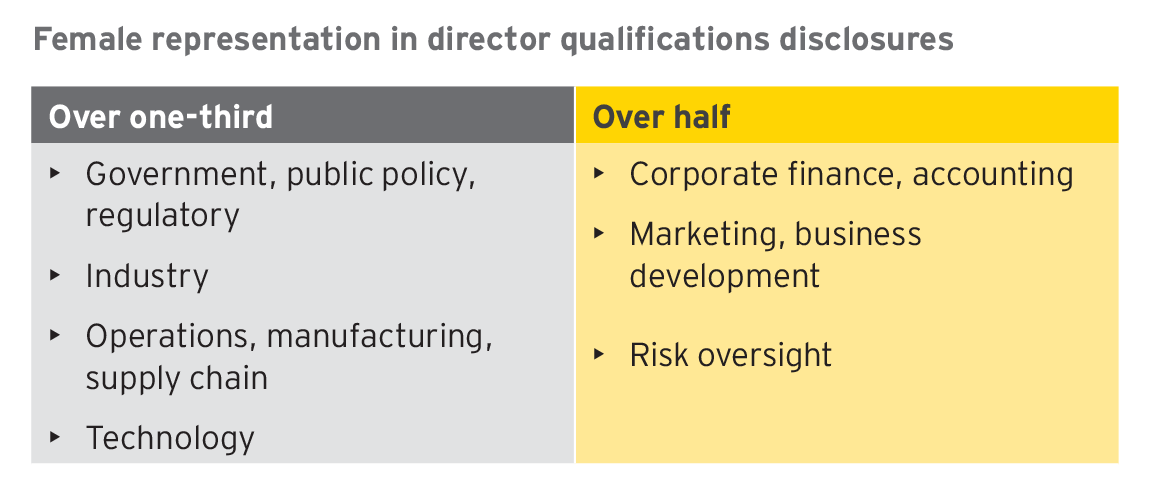
5. The class of 2017 is 40% female
As in the prior year, 40% of the entering class were women, but overall percentages were largely unchanged, with women directors averaging 28% board representation compared to 27% in 2016. Also, there was minimal age difference, with the women directors averaging 57 compared to 58 for male counterparts. Among the directors bringing the top categories of expertise, women directors accounted for over one-third of the disclosed director qualifications. In some cases, they represented over half of the disclosed category of expertise.
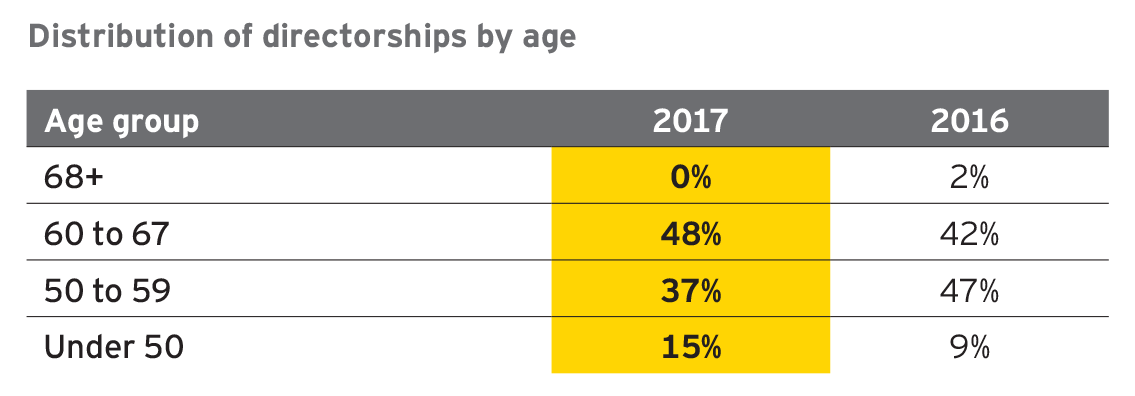
6. The class of 2017 tends to be younger
There appears to be an ongoing shift toward younger directors. For the class of 2017 entering directors, the average age of these individuals was 57, compared to 63 for incumbents and 68 for exiting directors. Of the entering class, 15% were under 50, an increase from 9% in the prior year. And, for the second consecutive year, we observe that over half of the entering class was under the age of 60. Exiting directors largely continue to be age 68 or older.
Questions for the board to consider
– How is the company aligning the skills of its directors—and that of the full board—to the company’s long-term strategy through board refreshment and succession planning efforts? How is the company providing voluntary disclosures around its approach in these areas?
– Does the company’s pool of director candidates challenge traditional search norms such as title, age, industry and geography?
– How is the company addressing growing investor and stakeholder attention to board diversity, and is the company providing disclosure around the diversity of the board—defined as including considerations such as age, gender, race, ethnicity, nationality—in addition to skills and expertise?
______________________________________________________________________________________
*Steve W. Klemash is Americas Leader, Kellie C. Huennekens is Associate Director, and Jamie Smith is Associate Director, at the EY Center for Board Matters. This post is based on their EY publication.